The Roles Of Visuals In Instructions :
- Visual can also motivate learners by attracting their attention, holding their attention, and generating emotional responses.
- Visual can simplify information that is difficult to understand.
- Visual provide a redundant channel.
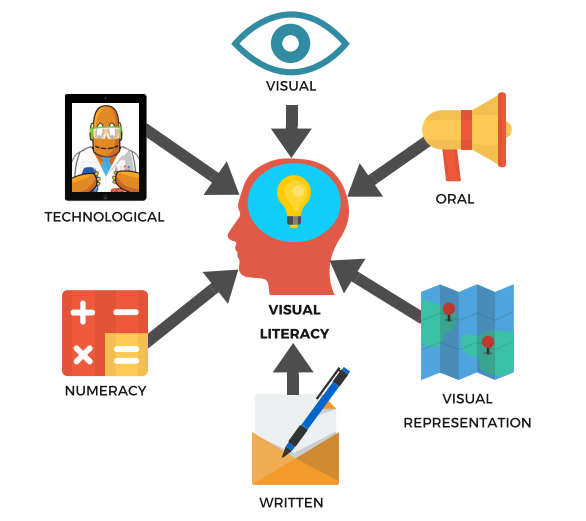
Visual Literacy
Consider the sorts of visuals that are used everyday for important communication purpose, such as the emergency information card in airplanes or highway signs that warm of dangerous curves or obstructions.
They work only to the extent that you are "literate" in the conversations of that medium. Whereas the term literacy once was used only to refer to reading and writing of verbal information, today we use the term visual literacy to refer to the learned ability to interpret visual messages accurately and to create such messages.
Visual Literacy can be developed through two majors approaches :
- Input strategies : Helping learners to decode, or "read" visual proficiently by practicing visual analysis skills (through picture analysis and discussion of multimedia and video programs).
- Output strategies : Helping learners to encode, or "write" to express themselves and communicative with other (through planning and producing photo and video presentation).
➣ Developmental Effects
Prior to the age of 12, children tend to interpret visuals section by section rather than as a whole, tend to summarize the whole scene and report a conclusion about the meaning of the picture.
Hence, abstract symbols or a series of still pictures whose relationship is not clearly spelled out many fail to communicative as intented with younger viewers.
➣ Cultural Effects
Different cultures groups may perceive visual material in different ways. Let's say your instructions includes visuals depicting scenes typical of the home life and street life of inner-city children. It is almost certain that students who live in such an area will decode these visual differently than will students whose cultural (and socioeconomic) backgrounds don't include firsthand knowledge of inner-city living.
➣ Visual Preferences
People don't necessarily learn best from the kinds of pictures they prefer to look at. Research on picture preferences indicates that children in upper elementary grades tend to prefer color to black and white and to choose photographs over drawing, younger children tend to prefer simple illustrations, whereas older children tend to prefer moderately complex illustrations. (Myair & Carter, 1979).
➤Encoding : Creating Visuals
Children who have grown up constantly exposed to movies and television may expect the visuals they encounter in school to be similary packaged and sequenced. They may need practice in arranging visuals into logical sequence, which is a learned skills, like the verbal sequencing in reading and writing. This chapter focuses on understanding visual design and doing visual displays into creative activities.
Visual Literacy Education
Media production, computer design and critical thinking skills can enhance students' abilities to work and succeeded in an increasingly visual world, ( diagram, hidden pictures, memory games, and video clips) to work alone or together on visual learning activities and develop communication, organization, and reporting skills in the process.
Goals Of Visual Design
- Ensure Legibility : The goal of good visual design is to remove as many obstacles as possible that might impose (spesific guidelines on, for example, the size of letters appear later in this chapter).
- Reduce Effort : You will see how establishing an understanding pattern (alignment, shape, balance), putting like things together (proximity), and following a regular pattern in your treatment (consistency) contribute to this goal. Using harmonious color combinations and figures that contrast with their background also play roles.
- Increase Active Engagement : Choosing a style appropriate for your audience and using appealing color schemes also will help you gain and hold your audience.
- Focus Attention : The overall design pattern plus spesific directional guides (woven into the design and color cues) are your means for achieving the goal of focusing attention.
Processes Of Visual Designs
- Elements : Selecting and assembling the verbal/visual elements to intercoporate into the display.
- Pattern : Choosing an underlying pattern for the elements of the display.
- Arrangement : Arranging the individual elements within the underlying pattern.
➤ Elements
We have grouped the following design suggestions according to the various elements or components of the display; the visual elements (choosing the type of the visual), the verbal elements (lettering style and location), and the elements that add appeal ( surprise, texture, interaction).
➣ Visual Elements
Realistic visuals show the actual object under study. Analysis visuals convey a concept or topic by showing something else and implying a similarity. Such visuals help learners interpret new information in light of prior knowledge and thereby facilitate learning.
➣ Verbal Elements
Most displays incorporate some type of verbal information in addition to visuals. At a minimum, you have to be sure that the lettering is legible in terms of size and spacing and of a style that is consistent with your intended message.
- Number of Lettering Styles : A display-or a series of related visuals, such as a slide series-should use no more than two different type styles, and these should harmonize with each other.
- Capitals : For best legibility, use lowercase letters, adding capitals only where normally required.
- Color of Lettering : As discussed later in the section "Figure-Ground Contrast", the color of the lettering should contrast with the background color both for the sake of simple legibility.
- Size of Lettering : Displays such as bulletin boards and posters are often meant to be viewed by people situated at a distance of 30 or 40 feet or more.
- Spacing Between Letters : The distance between the letter of the individual words must be judged by experience rather than on a mechanical basis.
- Spacing Between Lines : The vertical spacing between lines of printed material is also important for legibility.
➣ Elements That Add Appeal
Your visual has no chance of having an effect unless it captures and holds the viewer's attention.
➤ Pattern
The idea to establish pattern is to decide how the viewer's eye will flow across the display. The major factors that affect the overall look are alignment of elements, shape, balance, color, scheme, and color appeal.
➤ Visual Planning Tools
- Storyboards : Several related overhead transparencies, a slide set, a video sequence, or a series of computer screeens. This technique, borrowed from film and video production, allows you to creatively arrange and rearrange a whole sequence of thumbnail sketches.
- Types of Letters : The simplest is freehand lettering with markers and felt-tip pens, which come in an array of colors and sizes. You also may use an available dekstop publishing system to prepare lettering in various styles and sizes.
- Drawing, Sketching, and Cartooning : There are many sources of these in magazines, textbooks and advertising. Those are sources that can help you communicate effectively using those graphic media.
- Digital Images : As a computer technologies advance, creating visual images has moved into the digital camera to created original or may transfer images onto digital formats using scanners. Digital images allows users to capture, edit,display share and network still and video images.
- Digital Cameras : Digital cameras are small and lightweight with fewer moving parts than traditional cameras. Instead of aquinting thought a tiny optical view finder, most all cameras permit you to see a large images display on the back of the camera before you take the picture.
- Scanners : Scanners work with computer to transfer easisting visual images, such as drawing or photographs,students may quickly inscoeporate scanned images into a word processing file or enhance or change them using software.
Source : Heinich, Molenda, Russell, Smaldino et. All. 2002. Instructional Media and Technologies For Learning Volume 7. California: The University of California.